Reliability vs Validity: Differences, Types and Examples
May 6,22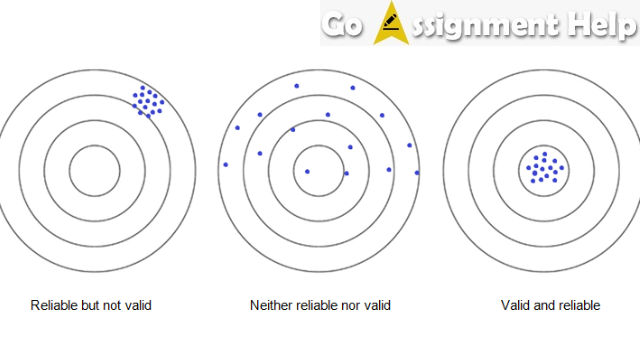
Reliability and validity are two important concepts in research. They represent the characteristics of an assessment tool that can determine whether it is a good instrument to study and measure the targeted variable. Many students ask us how these two compare with each other and how they are interrelated.
GoAssignmentHelp research writing experts explain that the former refers to consistency while the latter defines accuracy, so they are both essential criteria to assess data quality. Although reliability and validity have their own particularities, they are not unrelated. If reliability is high, validity is likely to be high as well.
Reliability and validity can be used in different forms of research, such as surveys or experiments. Therefore, it is important to define them correctly to understand how they work together. Additionally, it is essential for researchers to know that there are different types of reliability and validity that can be used in specific cases.
What is Reliability?

Reliability is the degree to which an assessment tool produces similar results under consistent conditions. In other words, it is the ability of a measure to produce stable and consistent results over time. There are several types of reliability, including:
- Internal consistency: This type of reliability assesses whether different items on a test measure the same thing. For example, if a math test has 30 questions and 20 of them are about algebra, internal consistency would be high. Cronbach’s alpha is a statistical tool that can be used to measure internal consistency.
- Split-half reliability: This measures the consistency of results between two halves of a test. For instance, if a test has 20 items and 10 items are randomly selected for one half and the other 10 for the second half, split-half reliability would be high if both halves produce similar results. The Spearman-Brown formula is used to calculate split-half reliability.
- Test-retest reliability: This assesses the stability of results over time. For example, if a test is given to a group of students and then again after a few weeks, test-retest reliability would be high if both results are similar. The Pearson correlation coefficient can be used to measure test-retest reliability.
- Interrater: This type of reliability assesses whether different raters or observers obtain similar results when using the same assessment tool. For example, if two teachers grading the same exam obtain the same results, interrater reliability would be high. Kappa statistic can be used to calculate this type of reliability.
What is Validity?

Validity is the extent to which an assessment tool accurately measures what it is intended to measure. In other words, validity refers to whether a measure captures the true construct that it is supposed to assess. There are several types of validity, including:
- Content validity: This type of validity assesses whether an assessment tool covers the entire construct that it is supposed to measure. For example, if a math test has questions about all the topics covered in a math class, content validity would be high.
- Criterion-related validity: This type of validity assesses whether an assessment tool predicts future performance on a criterion. For example, if a math test is correlated with performance in a math class, criterion-related validity would be high.
- Construct validity: This type of validity assesses whether an assessment tool measures the intended construct appropriately. For example, if a math test is correlated with higher grades on exams and assignments in a math class, construct validity would be high.
Although reliability and validity are two important concepts in research, it is important to note that neither one alone can guarantee the quality of an assessment tool. For this reason, researchers should carefully evaluate both reliability and validity when using an instrument to measure their data.
How are Reliability and Validity interrelated?
Although reliability and validity are two distinct concepts, they are closely related. In general, if a measure is reliable, it is likely to also be valid. This is because consistency and accuracy are both important factors in assessing data quality. However, even if an assessment tool has high reliability, that does not necessarily mean that it has high validity. It is possible for a measure to be reliable but not valid. Therefore, it is important for researchers to carefully consider both reliability and validity when developing or using an assessment tool.
For example, let’s say a researcher is conducting an experiment to examine the effectiveness of a new drug for treating depression. To measure the effects of the drug, she uses a standardized questionnaire that asks participants about their mood before and after taking the medication. Because this assessment tool has high internal consistency and test-retest reliability, it appears to be valid.
However, if the researcher fails to consider the construct validity of this questionnaire, she may not realize that it is only measuring compliance with treatment rather than actual changes in mood. As a result, her conclusions about the effectiveness of this drug may be inaccurate and misleading.
Some ways to ensure Reliability in your research work
- Using standardized and validated assessment tools whenever possible.
- Ensuring that all data is collected consistently, using the same procedures across participants or groups.
- Establishing clear protocols for administering assessments and managing data collection, including training of research staff as needed to ensure accuracy and consistency across measures.
- Conducting regular quality checks of data to identify any potential problems with reliability.
- Reporting measures of reliability (e.g., Cronbach’s alpha) in research papers to ensure transparency and replicability of results.
The aim while taking reliable measurements is to minimise measurement error. This will give you more confidence that the results of your study are true and accurate.
You may also check : 50 BEST FOOD RESEARCH PAPER TOPICS 2021
Some ways to ensure Validity in your research work
- Using multiple methods of assessment whenever possible, such as self-report questionnaires, interviews, and behavioural or physiological measures.
- Conducting thorough pilot testing of assessment tools to determine their validity and reliability under different conditions and with different populations.
- Consulting with experts in your field to obtain feedback on the appropriateness and effectiveness of assessment methods for your research questions.
- Consulting with subject matter experts to verify the accuracy and relevance of data interpretation and conclusions drawn from research results.
- Considering the theoretical grounding of your study, including relevant theories or models that may help explain relationships between variables in your data and guide future research questions or hypotheses.
There are many ways to ensure the quality of your research data. By carefully considering reliability and validity, you can help ensure that your research is accurate and informative.
Do you have any questions about reliability vs validity or how they impact your research? Let us know in the comments, and we’ll be happy to help!





0 responses on "Reliability vs Validity: Differences, Types and Examples"