Strategy Synthesis, Lenovo : Building a Global Brand
Sep 24,21Strategy Synthesis, Lenovo : Building a Global Brand
Question:
Describe About the Strategy Synthesis, Lenovo for Building a Global Brand?
Answer:
Introduction
An analysis of the case study on Lenovo making a global brand has indicated different major findings. The case analysis indicates that Lenovo has acquired IBM in order to go global and establish itself as a global brand. Initially, Lenovo was known as Legend and it has concentrated its focus only on the Chinese industry. But it has performed the acquisition of IBM to reflect its global business policy to make the brand a global brand (Bajarin, 2015). This case analysis focuses on different such important elements related to Lenovo’s decision of going global with the help of strategic analysis of “Lenovo”.
Overview of Company’s Strategy
Lenovo has built a strong brand image by emphasizing quality, innovation, and efficiency in its services and products. Lenovo, for example, was the first firm to launch a Chinese-character card, which has contributed considerably to the company’s growth. Furthermore, previous to the acquisition, the company’s emphasis was much localized, with all of its resources focused on Chinese markets. Lenovo has been able to achieve significant performance gains as a result of this. Before IBM’s purchase, all of these elements became the major contributors to Lenovo’s development and success (Nylander, 2016). Lenovo’s ability to respond to the particular demands and expectations of its Chinese clients has propelled the firm to new heights of growth and development.
Further, the business acquisition decision of Lenovo to get the PC business of IBM is also reflected in its global brand strategy. IBM had sold its company to Lenovo, and the case evaluation revealed that the most significant cause for IBM selling its business to Lenovo is primarily the agreement by Lenovo on the conditions as provided by IBM (Lenovo, 2021). For example, IBM held 8.9% of the newly acquired business even after the transaction. Lenovo has established itself as a significant supplier of personal computers in Chinese markets.
Application of SWOT Analysis
| Strengths
Ability to design language changing cards to users to convert English into Chinese |
Weaknesses
Developed brand image across Chinese markets |
| Opportunity
Innovation based new technology in the global market |
Threats
Rise in competition in PC industry due to the entry of HP and dell |
Analysis of Lenovo’s Strategy through Porter Five Forces
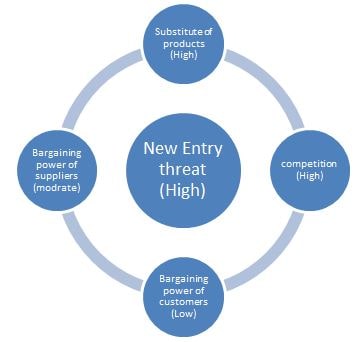
According to a study of the PC sector, buyers have more negotiating power since they have a wider range of options when it comes to choosing a brand, and this has resulted in suppliers having a medium bargaining strength (Verbeke, 2013). With the introduction of tablets and smartphones, the threat of replacement is also rising. However, the threat of a new entry is reduced due to the significant investment and reputation necessary to succeed in such a sector, and the competitive environment is highly difficult, with global companies such as Dell and HP battling fiercely (Rhally, 2014). In such market conditions, it is critical for Lenovo’s strategy to integrate both innovation and efficiency elements in order to effectively meet the rising competitive conditions that are widespread throughout worldwide marketplaces.
Analysis of Different Branding Strategies
Lenovo has examined some different branding techniques as part of its worldwide marketing efforts. The firm has a low degree of general recognition in foreign markets, and it has examined a variety of branding tactics to improve its level of awareness. The followings are some effective strategies that are used by Lenovo to make it’s brand a global brand:
Master Brand Strategy
This branding strategy forces the company to focus only on the master brand during its promotion (Fernando, 2021). This strategy allows the company to use all its resources in the development of a single brand in the market.
House of Brand Strategy
This branding approach invests resources in the development of each of the company’s sub-brands. It provides for a suitable degree of participation or attention from management to several corporate sub-brands, with none of them being overlooked (Han, 2018). This strategy may divert management’s attention away from a single brand strategy, but it will increase the company’s overall performance across all of its sub-brands.
Synergy Approach
Lenovo uses a synergy approach to promote its master brand in conjunction with a “hero” i.e. sub-brand. For example, the brand name IBM was used by Lenovo as a sub-brand to promote its master brand Lenovo (Lenovo, 2020). This strategy helps in getting a positive image of the sub-brand in the promotion of the master brand within target customers.
Effectiveness of Branding Strategies
Lenovo has considered a simple strategy to promote its brand. It has been identified that a simple strategy of one-two punch is being considered by Lenovo whereby the company focused on developing its Lenovo brand and continue to strengthen its ThinkPad product brand. This strategy as considered by Lenovo has been extremely effective from the point of view of catering to the needs and expectations of the brand. This is mostly due to IBM’s distinct image, whereas Lenovo has established its distinct brand in the Chinese market and is establishing its image in the worldwide market (Iide, 2021). But, the Chinese brand image of company is affecting its global image due to the bad performance of other Chinese products in the same market. As a result, the firm has benefited greatly from this basic approach of growing both of these brands such as IBM and Lenovo separately. Furthermore, Lenovo has emphasized the need of integrating innovation and efficiency in its brand, which has proven to be quite effective in handling the company’s increased level of competition (Verbeke, 2013). Overall, Lenovo’s branding approach has proven to be extremely effective.
Lenovo Becoming a Global Brand
Lenovo was initially a Chinese brand, according to the case study research, because it began operations in China. However, the firm eventually realized that it needed to become worldwide. In pursuing its global strategy, the company has encountered a number of issues. These issues are mostly due to the fact that Lenovo is primarily a Chinese brand, which is frequently linked with characteristics such as inferior quality. Furthermore, the case study of IBM revealed that the firm has never been able to face the heat of the competition with the help of lower product costs (Holstein, 2014). This is because that the brand image of the company is based on Chinese origin that reflects poor quality. As a result, such identification of the brand has had a negative impact on the firm’s ability to become a worldwide brand.
Recommendation to Overcoming Problems related to Brand
Issues faced by Lenovo in the concern of Chinese origin might be solved by concentrating on things such as quality. Lenovo may still become a big worldwide brand even if it adopted a cost-effective strategy, but it must focus on elements like innovation, greater quality, and so on to establish a distinct image among its customers (Verbeke, 2013). It must implement a localization strategy that would help it to get the local image for its product brand.
Conclusion
As per the above discussion, it concluded that the capacity of Lenovo to develop language converting cards as well as the ability of Lenovo to develop and deliver highly efficient goods and services to its consumers, have been recognized as key elements that have ascribed success to Lenovo in highly competitive global market. However, the analysis of the acquisition case of IBM by Lenovo has revealed that there are several significant challenges facing Lenovo’s performance following the acquisition, which are identified in terms of cross-cultural compatibility to address the demand of customers by managing the cultural differences with its to IBM. This report has also shown the benefits and drawbacks of Lenovo’s branding methods, and it has been concluded that Lenovo has had difficulty creating a worldwide brand because it is mostly based in China.
References
Bajarin, T. (2015). How a Chinese Company Became a Global PC Powerhouse. Retrieved from https://time.com/3845674/lenovo-ibm/
Fernando, J. (2021). A Look at Lenovo’s Strategy and Business Model. Retrieved from https://www.investopedia.com/articles/investing/073015/look-lenovos-strategy-business-model.asp
Han, G. (2018). Lenovo’s Brand Management Strategy – Promotion and Protection. Retrieved from http://www.chinaipmagazine.com/en/journal-show.asp?id=267
Holstein, W. (2014). Lenovo Goes Global. Retrieved from https://www.strategy-business.com/article/00274
Iide. (2021). Supercharged Case Study on Lenovo’s Digital Marketing Mix, Strategy and Competitors. Retrieved from https://iide.co/case-studies/lenovo-marketing-strategy/
Lenovo. (2020). Collaboration Experiences Need to Work in Synergy with a Highly Distributed Workforce. Retrieved from https://news.lenovo.com/collaboration-experiences-need-to-work-in-synergy-with-a-highly-distributed-workforce/
Lenovo.(2021). Lenovo Marks Decade of Success Since Acquisition of IBM’s PC Business. Retrieved from https://news.lenovo.com/pressroom/press-releases/lenovo-marks-decade-success-since-acquisition-ibms-pc-business/
Nylander, J. (2016). How Lenovo Became The Largest PC Maker In The World. Retrieved from https://www.forbes.com/sites/jnylander/2016/03/20/how-lenovo-became-the-largest-pc-maker-in-the-world/?sh=1e5c4445388b
Qiao, G. and Conyers, Y. (2014). The Lenovo Way: Managing a Diverse Global Company for Optimal Performance. McGraw Hill Professional.
Rhally, C. (2014). Don’t Say You’re a Chinese Company: How Lenovo Grew as a Global Brand. Retrieved from http://projourno.org/2014/04/dont-say-youre-a-chinese-company-how-lenovo-grew-as-a-global-brand/
Verbeke, A. (2013). International Business Strategy. Cambridge University Press.





